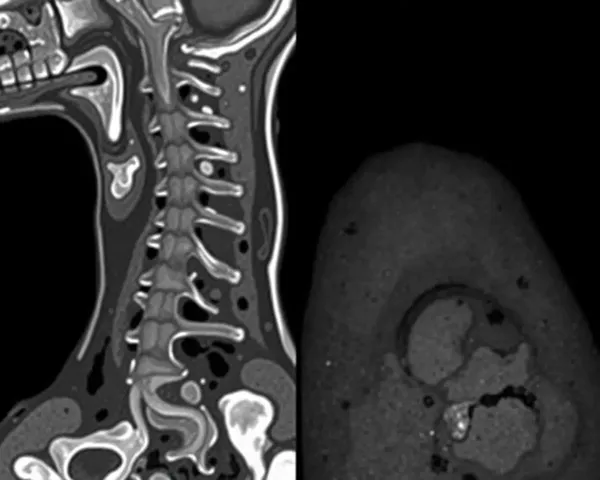
nuclear imaging(544)
s internal structures and functions. It involves the injection of a radioactive substance, known as a radiopharmaceutical, into the patient
Top Recommended Prompts
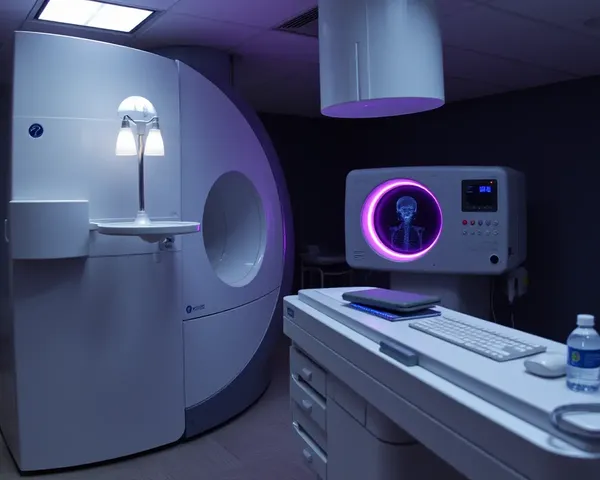
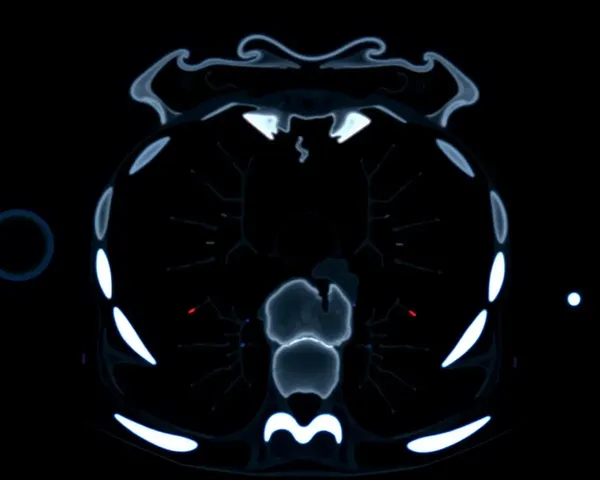
A detailed diagram of the principles of single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT) imaging, including the injection of radiopharmaceuticals, detection of gamma rays, and reconstruction of 3D images of the body's internal structures and functions.
A 3D rendering of a brain scan using functional magnetic resonance imaging (fMRI) and positron emission tomography (PET) to visualize the neural connections and activity of a person's brain, highlighting the intricate networks and pathways that enable thought, emotion, and movement.
A futuristic illustration of a nuclear medicine department in a hospital, showcasing various machines and technicians working together to create detailed images of the human body using nuclear imaging techniques such as positron emission tomography (PET) and single photon emission computed tomography (SPECT).